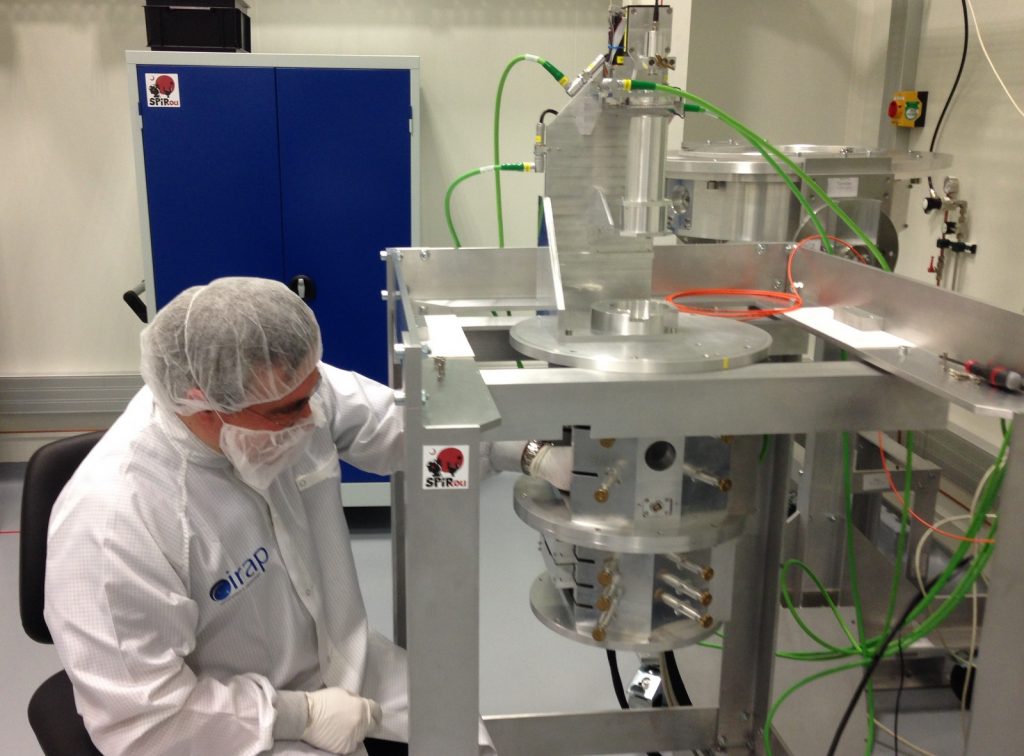
2016 November: Optical alignment of the Cassegrain unit at IRAP/OMP
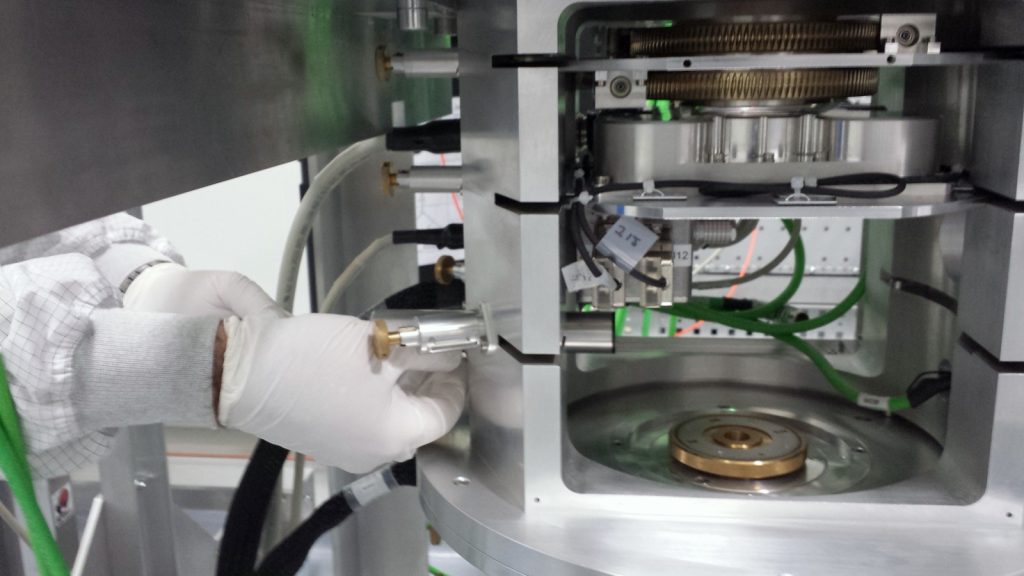
The optical components of the Cassegrain unit are being integrated and aligned
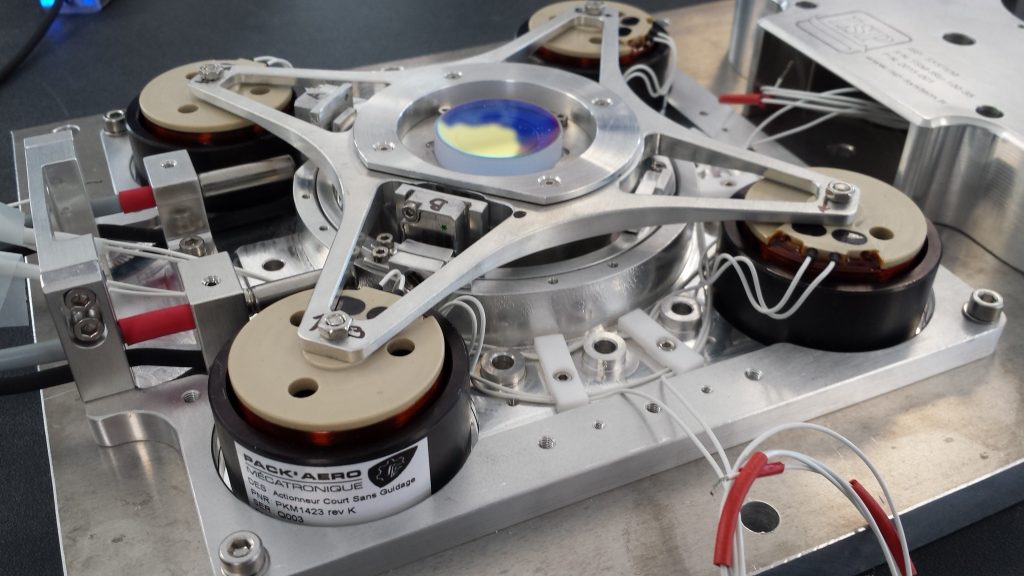
The SPIRou Cassegrain unit includes precision optics, some of which specifically aimed at measuring the polarization of the incoming stellar light.

The Cass unit is made of an upper and lower module, the first one dedicated to calibration and atmospheric correction facilities, the second one to the polarimetric analysis of the incoming stellar light.
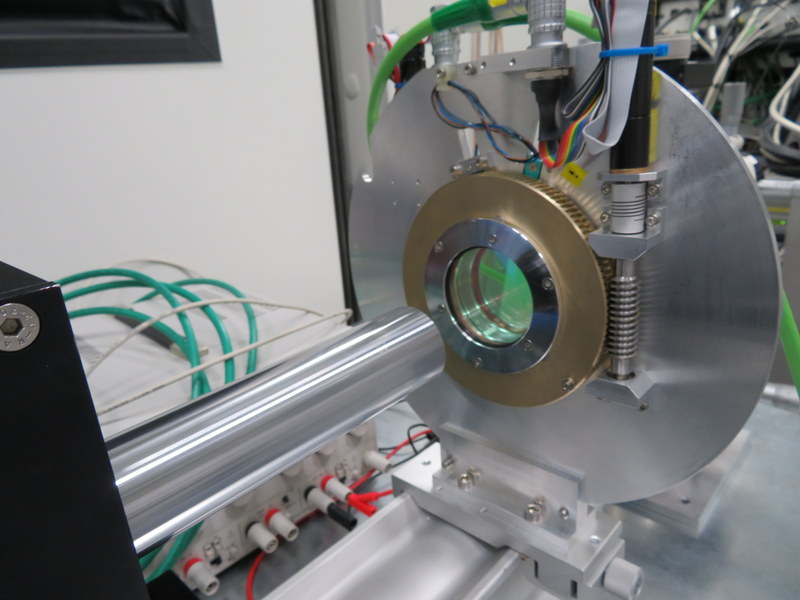
The first step in the alignment procedure deals with the polarimetric module; it consists in retro-illuminating the polarimetric module of the Cass unit through the output fibers, and in making sure that the light coming from the fibers is well focused on the entrance aperture of the polarimeter. This entrance aperture can be scrutinized using the guiding channel and camera (part of the upper Cass unit), with a specific device allowing us to redirect light from the polarimetric unit to the guiding channel. The upper Cass unit also includes an atmospheric dispersion corrector (ADC), as well as a tip-tilt module to ensure image stabilization at the entrance of the instrument, whereas the lower Cass unit features a cold stop aimed at blocking thermal emission from the telescope. Once fully integrated, the Cass unit will be tested at cold temperatures (down to -10 °C) within the dedicated climatic chamber available in the clean room.
This alignment procedure (as well as the forthcoming tests of the instrument) requires the use of an artificial star simulating the beam at the Cass focus of the CFHT, as well as atmospheric dispersion, turbulence and seeing. These activities are handled by Laurent Parès, Marie Larrieu and Michel Dupieux from IRAP/OMP.