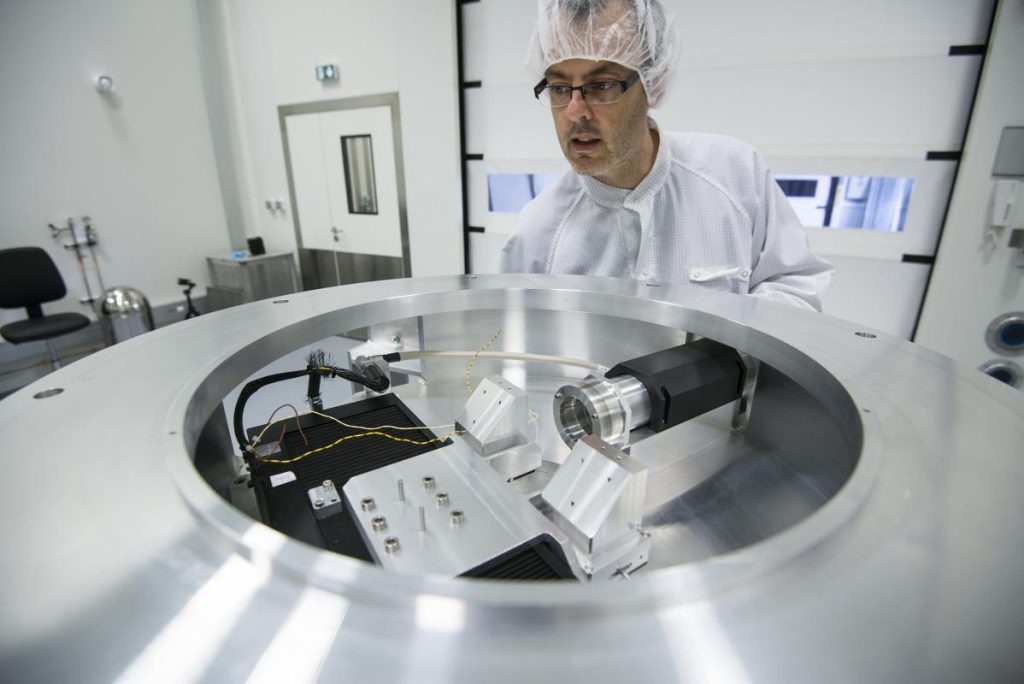
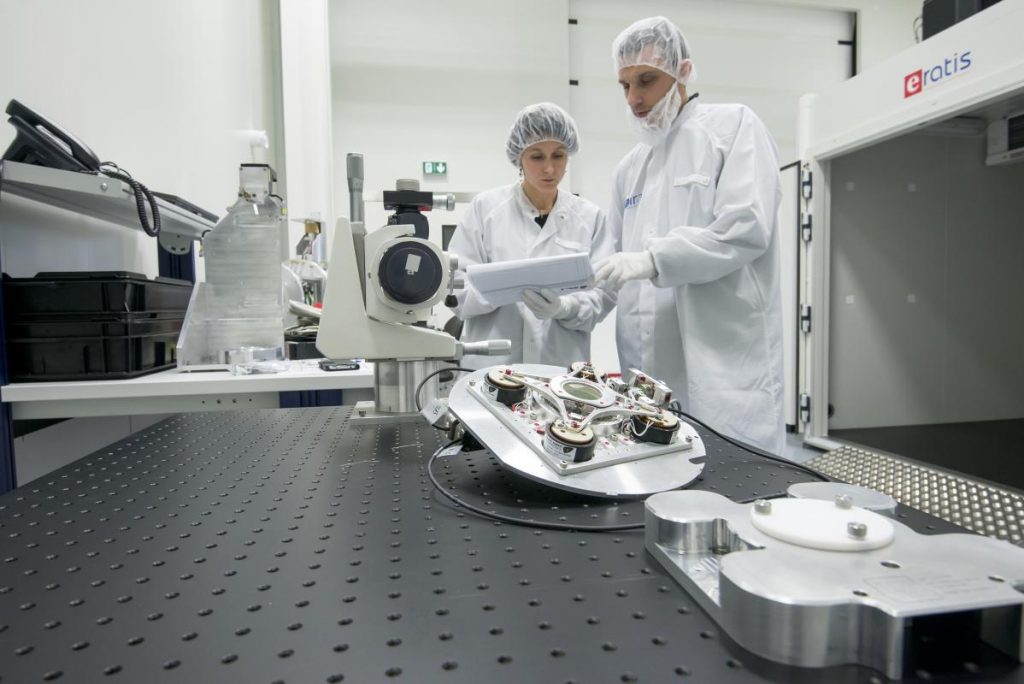
2016 March: Integration of the SPIRou Cassegrain module at IRAP/OMP
The three sections of the SPIRou Cassegrain module are being assembled and tested at IRAP/OMP
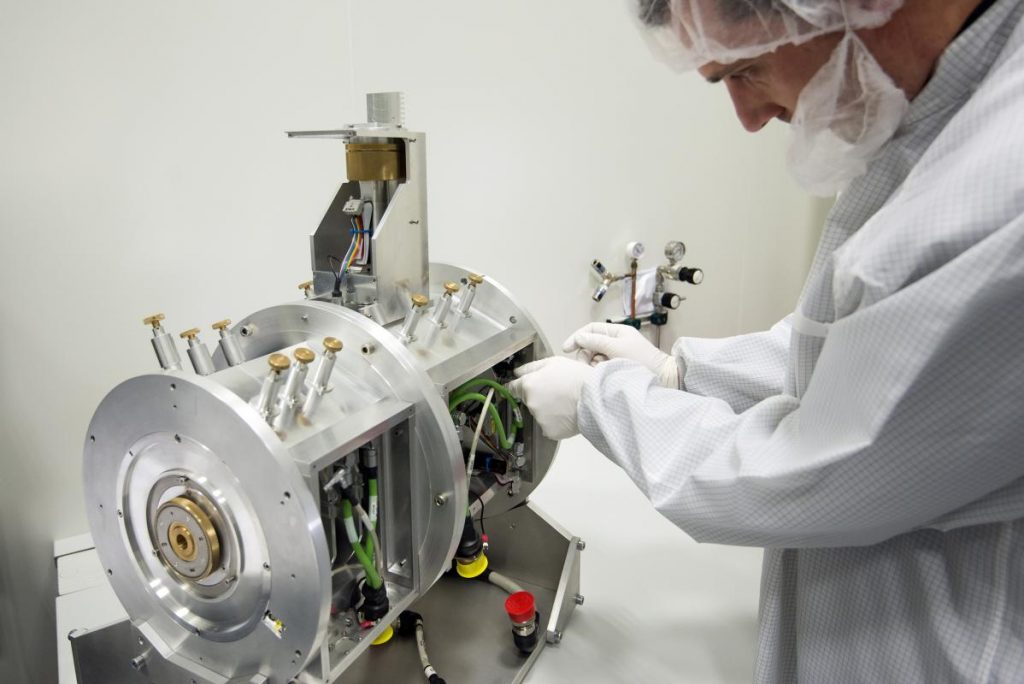

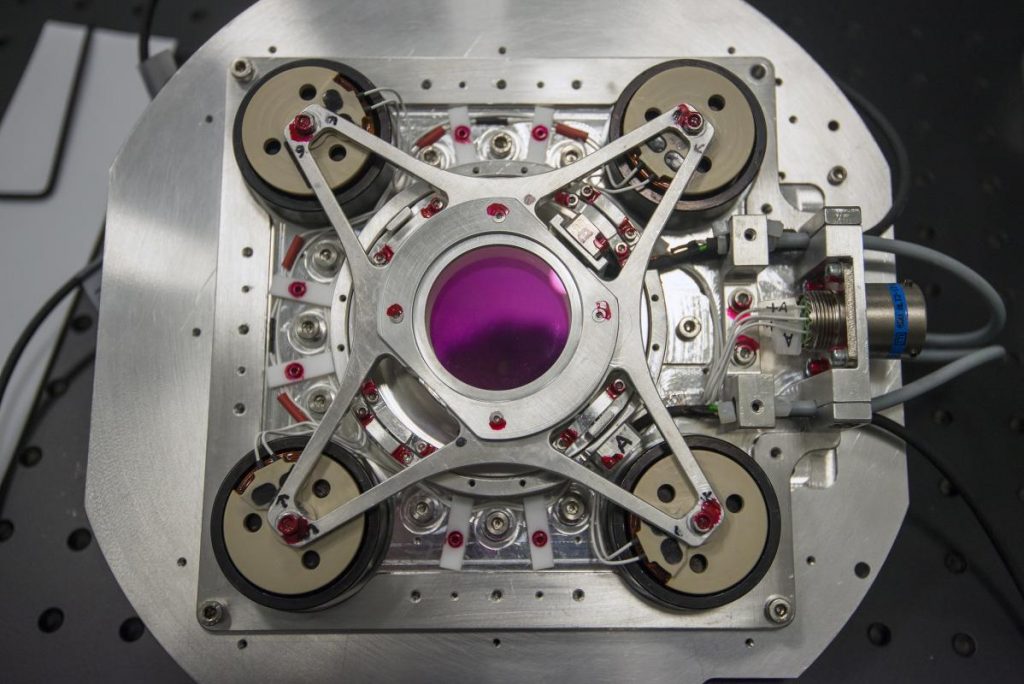
The SPIRou Cassegrain module is currently being integrated and tested in the P2IS clean room at IRAP / OMP. This module splits into three separate sections:
- the upper section interfacing SPIRou with the telescope and containing some calibration devices,
- the middle section, correcting for atmospheric dispersion and including tip-tilt / guiding facilities thanks to which the image of the star to be observed is stabilized with respect to the instrument entrance aperture (by correcting for the image motions caused by atmospheric turbulence and telescope instabilities),
- the lower section consisting of a polarimetric unit, performing an achromatic polarimetric analysis of the incoming stellar light and splitting the main beam into 2 orthogonally polarized beams to be injected in fluoride fibers that convey the light to the SPIRou cryogenic spectrograph.
The Cassegrain module, whose electromechanical behavior is currently being tested down to temperatures of -10° in the dedicated climatic chamber of the IRAP / OMP clean room, will soon integrate all optical components that have already been (or are about to be) delivered to IRAP – in particular the atmospheric dispersion corrector, the Image Stabilization Unit, the viewing / guiding nIR Raptor camera, the input / output focal reducers, the Wollaston prism, and a pair of super-achromatic Fresnel rhombs.